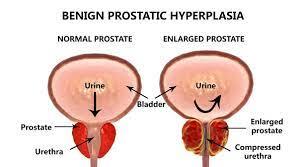
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, is the most frequent benign tumour detect in men, and Kamagra 100mg Oral Jelly is the best treatment for it.
BPH, like prostate cancer, is more common in the West than in Eastern countries like Japan and China, and it may be more common in black people. A recent study discovered a possible genetic relationship for BPH in males under the age of 65 who have a severely enlarged prostate: Their male relatives were four times more likely than other men to require BPH surgery at some point in their lives, while their brothers were six times more probable.
BPH causes symptoms by restricting urine passage through the urethra. Symptoms of BPH are evident in one out of every four men by the age of 55, and in half of men over the age of 75. However, treatment is only require if symptoms become unbearable. By the age of 80, 20% to 30% of men have BPH symptoms severe enough to necessitate treatment. Until the recent approval of minimally invasive treatments that open the prostatic urethra and medications that can ease symptoms by decreasing the prostate or relaxing the prostate muscular tissue that constricts the urethra, surgery was the sole option.
Symptoms and Signs
BPH symptoms are classified as either those induced directly by urethral blockage or those caused by subsequent bladder alterations.
Trouble starting to urinate despite pushing and straining
A weak stream of urine; multiple interruptions in the stream
Dribbling at the end of urination
Bladder alterations cause:
An unexpected urgent desire to urinate (urgency)
Frequent urination
The sense that the bladder is not emptied after urination
Numerous nighttime awakenings to urinate (nocturia)
A guy may become incontinent as his bladder grows more sensitive to retained urine (unable to control the bladder, causing bed wetting at night or inability to respond quickly enough to urinary urgency).
If you have a bladder tumour, infection, or stone, you may experience burning or pain while urinating. Although blood in the urine (hematuria) may indicate BPH, most men with BPH do not have hematuria.
Diagnosis and screening
The American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index provides an objective assessment of BPH symptoms, which aids in therapeutic decision-making. This score, however, cannot be utilise for diagnosis because other disorders might present symptoms identical to BPH.
A medical history will reveal any disorders that may be mistake for BPH, such as urethral stricture, bladder cancer or stones, or aberrant bladder/pelvic floor function (issues hold or emptying pee) cause by a neurologic disorder (neurogenic bladder) or pelvic floor muscular spasms. Strictures can occur as a result of urethral injury caused by trauma, equipment (such as catheter insertion), or an infection such as gonorrhoea. If there is a history of blood in the urine, bladder cancer is suspect
Treatment
When is BPH treatment require?
The progression of BPH in any individual is unpredictable. According to certain research, symptoms and objective assessments of urethral blockage can remain stable for many years and may even improve with time for up to one-third of men. Urinary symptoms did not worsen in 73% of men with mild BPH over a 3.5-year period, according to a Mayo Clinic study. The symptoms most associated with the ultimate requirement for treatment are a steady decrease in the size and force of the urine stream, as well as the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying. Although nocturia is one of the most bothersome BPH symptoms, it does not indicate the need for future treatment.
If a deteriorating urethral obstruction is not address, the following consequences may occur:
a thickened, irritable bladder with reduced pee capacity; infected residual urine or bladder stones; and a pressure backing that affects the kidneys.
Treatment is determine by the severity of symptoms (as measure by the AUA Symptom Index), the extent of urinary tract damage, and the man’s overall health. In general, no treatment is recommend for people who only experience a few symptoms and are not concerned by them. In the following situations, intervention — usually surgical — is require
Inadequate bladder emptying resulting in kidney damage
Complete inability to urinate after acute urinary retention
Incontinence due to overfilling or increased sensitivity of the bladder
Bladder stones
Infected residual urine Recurrent severe hematuria
• Symptoms that bother the patient enough to reduce his quality of life
For males with mild symptoms, treatment decisions are more complicated. They must assess the risks of treatment against the severity of their symptoms. Each person must decide whether his symptoms are bothering him enough to warrant treatment. While deciding on a treatment, both the patient and the doctor must weigh the effectiveness of various forms of therapy against their adverse effects and expenses.
BPH Therapy Options
Presently, the primary alternatives for treating BPH are:
Medication
Long-term medical therapeutic advantages and potential side effects are still being studied. Today, medications like sildenafil citrate and Malegra 200 are use to treat BPH. According to preliminary study, these medications help symptoms in 30% to 60% of men, but it is not yet possible to anticipate who will react to medical therapy or which drug will be better for an individual patient.
Surgery
Prostate surgery involves the displacement or removal of the obstructive adenoma of the prostate. Historically, surgical procedures were reserve for men who had failed medical therapy and experienced urinary retention due to BPH, recurrent urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or prostate bleeding. Yet, due to side effects, a huge number of men do not adhere to medical therapy. For these men, surgical therapy may be consider to prevent long-term impairment of bladder function.
Transurethral incision of the prostate, bipolar transurethral vaporisation of the prostate (TUVP), photo selective vaporisation of the prostate (PVP), prostatic urethral lift (PUL), thermal ablation using transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT), water vapour thermal therapy, and transurethral needle ablat
VISIT : geekshub.net